Midterm Practice Problems
Solutions will be posted under Other Content on Blackboard on Saturday morning.
These problems are not comprehensive, so make sure to review all of the relevant materials.
I. The Basics through Recursion
-
What is the output of the following Java code fragment?
int a = 7; int b = a / 2; double c = a / 2; double d = a / 2.0; String e = "b" + a; System.out.println("a = " + a); System.out.println("b = " + b); System.out.println("c = " + c); System.out.println("d = " + d); System.out.println("e = " + e);
-
What is the output of the following Java program?
public class Problem2 { public static void method1() { System.out.print("X "); } public static void method2() { System.out.print("Y "); } public static void main(String[] args) { for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) { if (i <= 2) { method1(); } else { method2(); } } } }
-
What is the output of the following?
int i, j; for (i = 0; i <= 4; i += 2) { for (j = 1; j < i; j++) { System.out.println(i + " " + j); } System.out.println(i + j); }
-
What is the output of the following Java program?
public class Problem4 { public static void main(String[] args) { int x = 1; int y = 2; int z = 3; z = mystery(x, z, y); System.out.println(x + " " + y + " " + z); mystery(y, y, x); System.out.println(x + " " + y + " " + z); } public static int mystery(int z, int x, int y) { z--; x = 2*y + z; y = x - 1; System.out.println(x + " " + y + " " + z); return x; } }
-
What is the output of the following code fragment?
int val = 14; if (val < 10 && val <= 20) { System.out.println("bye"); } else if (val != 10) { System.out.println("eek"); if (!(val < 10)) { System.out.println("ack"); } } else if (val >= 10) { System.out.println("bat"); } if (val / 2 == 7) { System.out.println("yak"); }
-
Write a static method named
processNamethat takes as a parameter a string representing a name and does the following:-
If the name is a one-word name (e.g., “Oprah” or “Bono”), the method should return the number of characters in the name.
-
If the name has more than one word (e.g., “Barack Obama” or “Sarah Jessica Parker”), the method should return the number of spaces in the name.
For example:
processName("Oprah")should return5processName("Bono")should return4processName("Barack Obama")should return1processName("Sarah Jessica Parker")should return2
You may assume that multi-word names have one space between each pair of words in the name, and that there are no leading or trailing spaces in the string.
-
-
What is the output of the following Java program?
public class Problem6 { public static void main(String[] args) { int[] x = {5, 6, 7}; int y = 4; mystery(x, y); System.out.println(Arrays.toString(x) + " " + y); } public static void mystery(int[] z, int y) { for (int i = 0; i < z.length; i++) { z[i] += y; } y *= 2; System.out.println(Arrays.toString(z)); } }
-
Write a static method
minGapthat takes an array of integers as a parameter and that returns the minimum gap between adjacent values in the array. The gap between two adjacent values in an array is defined as the second value minus the first value. For example, suppose that you have the following array:int[] values = {1, 3, 7, 2, 12};
The first gap is
2(3-1), the second gap is4(7-3), the third gap is-5(2-7), and the fourth gap is10(12-2).Thus, the call
minGap(values)should return-5, because that is the smallest gap in the array. Note that we are not taking the absolute values of the gaps before we compare them, which is why a gap of -5 is smaller than gaps of 2 or 4.If the method is passed an array with fewer than 2 elements, it should return 0.
-
Consider the following lines of Java code:
int[] a = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; int[] b = {5, 4, 3, 2, 1}; int[] c = a; for (int i = 0; i < b.length; i++) { c[i] = b[i]; } b[3] += b.length; a[3]--; System.out.println(a[3] + " " + b[3] + " " + c[3]);
-
Draw a single memory diagram that shows the final result of these lines. Include both the stack and the heap in your diagram. You may assume that these lines are part of the
mainmethod. -
Indicate what will be printed by the final line of code shown above.
-
-
Write a static method
shiftRightthat takes an array of integers and shifts all of the array elements one position to the right, with the original last element wrapping around to become the new first element. For example, consider this array:int[] values = {0, 2, 4, 6, 8, 10};
After calling
shiftRight(values), the contents of thevaluesarray should be{10, 0, 2, 4, 6, 8}. -
Write a method with the header
public static int indexOf(int[] arr1, int[] arr2)
that takes two arrays of integers and that returns the index of the first occurrence of the sequence represented by the first array in the second array, or -1 if the sequence represented by the first array does not appear in the second array. For example, suppose that you have these arrays:
list1: {1, 3, 6} list2: {1, 3, 5, 8, 12, 1, 3, 17, 1, 3, 6, 9, 1, 3, 6}
then the call
indexOf(list1, list2)should return8because the first occurrence of the sequence of values inlist1appears inlist2starting at index 8. You may assume that both arrays have at least one element. -
Write a mutator for the
Rectangleclass from lecture that doubles the width of aRectangleobject. -
What is the output of the following Java code fragment?
Rectangle r1 = new Rectangle(5, 10); Rectangle r2 = new Rectangle(5, 10); Rectangle r3 = r2; System.out.println((r1 == r2) + " " + (r2 == r3));
-
Create a Java class called
Triangle. The class should have:-
two floating-point fields: one for the base of the triangle and one for its height
-
a constructor that takes an initial value for each of the fields
-
accessor and mutator methods for each field
-
a method called
areathat computes and returns the area of the triangle, which should be a floating-point value that is 0.5 times the product of its base and height. -
an appropriate
toString()method. For example:> Triangle t = new Triangle(3.0, 4.0); > System.out.println(t); triangle with base 3.0 and height 4.0
-
an appropriate
equals()method, that can be used to determine if twoTriangleobjects have the same base and same height.
Make sure to employ appropriate encapsulation. Protect the fields from direct access by clients, and make sure that only positive values are assigned to the fields.
-
-
Write a client program for your
Triangleclass. Put it in a class calledTriTester, and give it two methods:-
a static method called
processTriangle()that takes aTriangleobject as a parameter, prints it, and prints its area. For example:> Triangle t = new Triangle(3.0, 4.0); > TriTester.processTriangle(t); triangle with base 3.0 and height 4.0 (area = 6.0)
Take advantage of the methods in the
Triangleobject. -
a
main()method that does the following:-
creates three
Triangleobjects:tri1(with base 3.0 and height 4.0),tri2(with base 6.0 and height 6.0), andtri3(also with base 3.0 and height 4.0) -
uses `processTriangle() to process each of the triangles
-
tests whether
tri1andtri2are equal and reports the result -
tests whether
tri1andtri3are equal and reports the result.
-
Here is the desired output of the program:
tri1: triangle with base 3.0 and height 4.0 (area = 6.0) tri2: triangle with base 6.0 and height 6.0 (area = 18.0) tri3: triangle with base 3.0 and height 4.0 (area = 6.0) tri1 and tri2 are not equal tri1 and tri3 are equal
-
-
Write a subclass of
TrianglecalledEquilateralTriangle. Its constructor should take a single parametersiderepresenting the length of a side. However, the new class should not have any new fields. Rather, it should use the attributes that are inherited fromTriangle, and you should initialize those attributes by calling the superclass constructor and passing it the appropriate values. (You should approximate the height of the triangle as 0.866 times the side length.) For example:> EquilateralTriangle tri1 = new EquilateralTriangle(6.0); > System.out.println(tri1); triangle with base 6.0 and height 5.196
-
Override the appropriate method in
EquilateralTriangleso that printing anEquilateralTriangleobject produces an output that looks like the following instead:> EquilateralTriangle tri1 = new EquilateralTriangle(6.0); > System.out.println(tri1); equilateral triangle with side 6.0
Questions 18-20 are based on the following Java classes:
public class A extends B { public void twist() { System.out.println("ho!"); } } public class B { public void twist() { System.out.println("ouch!"); } public void shout() { System.out.println("oh!"); } } public class C extends A { public void gasp() { System.out.println("why?"); } }
-
You create the following objects of the above classes:
A a1 = new A(); B b1 = new B(); C c1 = new C();
(Note: The above constructor calls are fine, because Java gives us a constructor with no parameters when we don’t define our own constructor.)
Explain why each of the following method calls either would or would not compile:
a1.shout() a1.gasp() b1.twist() c1.toString()
-
Given the objects created in the previous problem, what would the output be of the following statements?
c1.twist(); c1.shout();
-
Given the above class definitions, which of the following assignment statements would be allowed, and which would not be allowed?
A a1 = new C(); A a2 = new B(); B b1 = new C(); Object o = new A();
Explain your answers briefly.
-
Recall the
ArrayBagclass from lecture. Give this class an accessor method calledcount()that takes an arbitrary objectitemand returns the number of times thatitemoccurs in theArrayBag. -
Consider the following method:
public static int test(int a, int b) { if (a < b) { return 0; } else { return 1 + test(a-b, b); }
What is returned by the call
test(15, 4)?How many times is the method called during the execution of
test(15, 4)– including the initial call? -
Write a recursive static method named
sumReciprocalsthat takes as its only parameter an integernthat you can assume is positive, and that uses recursion (no loops!) to compute and return a floating-point value that is the sum of the reciprocals of the integers from 1 ton. For example,sumReciprocals(2)should return1.5, which is1/1 + 1/2, andsumReciprocals(4)should return approximately2.0833, which is1/1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/4. -
Write a recursive static method called
removePadding()that takes a stringsand that uses recursion to return a new string in which all leading and trailing spaces have been removed. For example,removePadding("hello world")should return"hello world".
II. Big-O through linked lists
Questions 1-3 involve the following method:
public static int mystery(int a[]) { int n = a.length; int result = 0; for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) { int x = a[i]; // Question 2 int sum = 0; for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) { sum *= a[i]; // Question 3 } result += sum; int j = i; while (j > 0) { result += a[j]; // Question 4 j--; } } return result; }
-
What is the big-O expression for the number of times that the line
int x = a[i];
is executed?
- O(n)
- O(n²)
- O(n log(n))
- O(log(n))
- O(n!)
-
What is the big-O expression for the number of times that the line
sum *= a[i];
is executed?
- O(n)
- O(n²)
- O(n log(n))
- O(log(n))
- O(n!)
-
What is the big-O expression for the number of times that the line
result += a[j];
is executed?
- O(n)
- O(n²)
- O(n log(n))
- O(log(n))
- O(n!)
-
The following array is to be sorted using insertion sort:
{18, 10, 8, 35, 9, 29, 5}Which of the following shows the contents of the array at the end of one of the iterations of the algorithm?
{ 5, 10, 8, 35, 9, 29, 18}{ 5, 8, 9, 35, 10, 29, 18}{ 8, 9, 10, 35, 18, 29, 5}{ 8, 10, 18, 35, 9, 29, 5}{10, 8, 18, 9, 29, 5, 35}
-
Here is an array that has just been partitioned by the first step of quicksort:
{3, 0, 2, 4, 5, 8, 7, 6, 9}Which of the following statements is correct?
5could be the pivot, but7could not be.7could be the pivot, but5could not be.- Neither
5nor7could be the pivot. - Either
5or7could be the pivot.
-
The following array is to be sorted:
{19, 22, 11, 13, 53, 34, 25}Which of the algorithms that we discussed in lecture will cause the array to be ordered as follows
{19, 11, 13, 22, 34, 25, 53}at an intermediate stage in the sorting process?
- insertion sort
- bubble sort
- quicksort (with an initial pivot of 13)
- selection sort
- merge sort
-
Through experiment, you determine that selection sort performs 5000 comparisons when sorting a array of some size k. If you doubled the size of the array to 2k, approximately how many comparisons would you expect it to perform?
- 5000
- 10000
- 20000
- 40000
- it would depend on the contents of the array
-
Through experiment, you determine that selection sort performs 5000 moves when sorting a array of some size k. If you doubled the size of the array to 2k, approximately how many moves would you expect it to perform?
- 5000
- 10000
- 20000
- 40000
- it would depend on the contents of the array
-
Ignore this question: Which of the following statements is not true about the increments used in Shell sort?
- The increments should be decreasing.
- The increments should be relatively prime.
- The final increment should be 1.
- The increments should be prime numbers.
Questions 10 and 11 involve linked lists of integers that are constructed from nodes whose class definition begins as follows:
public class Node { private int val; private Node next; public Node() { this.val = 0; this.next = null; } ... }
-
You want to add a method to the
Nodeclass that takes two parameters:-
a reference to the first node in a linked list (or
nullif the list is empty) -
an integer
x
The method should insert a node containing
xat the front of the list, and it should return a reference to the new front of the list.Which of these methods does this correctly?
option I:
public static Node insertFront(Node first, int x) { first = new Node(); first.val = x; first.next = first; return first; }
option II:
public static Node insertFront(Node first, int x) { Node n = new Node(); n.val = x; n.next = first; return n; }
option III:
public static Node insertFront(Node first, int x) { Node n = new Node(); first = n; n.val = x; n.next = first; return first; }
- only I
- only II
- only III
- I and II, but not III
- II and III, but not I
-
-
The intent of the method below is to delete the last node in the linked list to which the parameter
firstrefers:public static void removeLast(Node first) { Node p = first; Node q = p.next; while (q.next != null) { p = q; q = q.next; } p.next = null; }
Which of the following describes the subset of linked lists for which this method works correctly?
- no linked lists
- all nonempty linked lists
- all linked lists with more than one node
- the empty list and all linked lists with more than one node
- all linked lists
-
A doubly linked list is constructed from nodes that are instances of the following class:
public class DNode { private char ch; private DNode next; private DNode prev; }
The
nextfield holds a reference to the next node in the linked list, and theprevfield holds a reference to the previous node in the linked list.Below is a list of three of these nodes, along with two reference variables,
nandp, that refer to specific nodes in the list: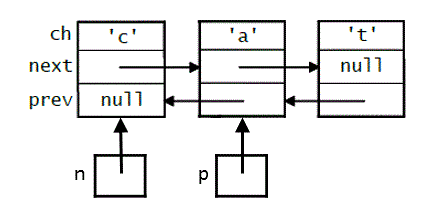
Which of the following expressions does not refer to the third node in the list?
p.nextn.next.nextp.prev.nextp.prev.next.nextn.next.next.prev.next
-
The diagram below suggests how we could implement a linked list in which we maintain a reference to both the first and last nodes in the linked list:
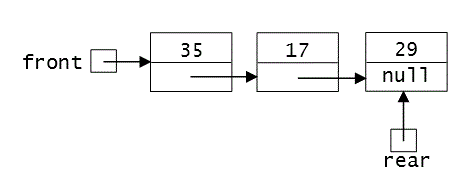
Which of the following operations would be inefficient to carry out when there are a large number of elements in the linked list?
- insertion at the end to which
frontrefers - insertion at the end to which
rearrefers - deletion from the end to which
frontrefers - deletion from the end to which
rearrefers
- insertion at the end to which
-
The following array is to be sorted:
{17, 53, 71, 36, 46, 41, 23, 12}-
During the execution of quicksort, what would the array look like after the first call to the
partition()method? -
During the execution of quicksort, what would the array look like after the second call to the
partition()method? -
After the initial pass of bubble sort, how would the array be ordered?
-
Ignore this question: Assume that the initial phase of Shell sort uses an increment of 3. At the end of that phase, how would the array be ordered?
-
After three passes of selection sort, how would the array be ordered?
-
After four passes of insertion sort, how would the array be ordered?
-
During the execution of mergesort, what would the array look like after the third call to the
merge()method?
-
-
The diagram below shows a linked list of characters that is constructed from instances of the
StringNodeclass from lecture: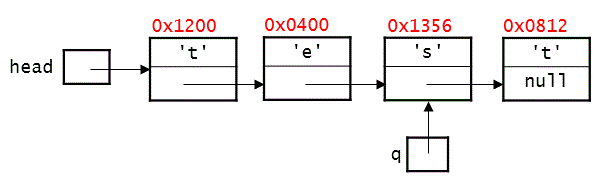
In addition, we have included two variables that each store a reference to one of the nodes in the linked list, along with the memory address of each node. You should assume that the
chfield has the same address as the node itself, and that the address of thenextfield is 2 bytes after the beginning of the node.-
What is the memory address of the field given by the expression
head.next.next? -
What is the value of the expression
head.next.next? -
Write one or more lines of code that remove the node containing the character
's'from the list. -
Modify the diagram to reflect the results of executing the following lines on the original version of the list (before the
's'was removed):q = q.next; q.next = head;
-
-
This question involves linked lists of integers that are constructed from nodes of the following class:
public class Node { private int val; private Node next; }
-
Write a static method named
numEvenRec()that takes a reference to the first node in a linked list of integers and uses recursion to determine and return the number of even values in the list. -
Write a static method named
numEvenIter()that takes a reference to the first node in a linked list of integers and uses iteration to determine and return the number of even values in the list.
-
-
Write a static method called
everyOther()that is a member of theStringNodeclass. It should take a reference to the first node in a linked-list string, and it should create and return a reference to a new linked-list string that contains every other character from the original string. The original linked list should not be modified. You may use either recursion or iteration.